You'll be able to configure our .NET agent to suit your environment after you create a New Relic account (it's free, forever) and install the .NET agent.
Configuration overview
APM agent configuration options allow you to control some aspects of how the agent behaves. Some of these config options are part of the basic install process (like setting your license key and app name), but most are more advanced settings, such as setting a log level, setting up proxy host access, excluding certain attributes, and enabling distributed tracing.
The .NET agent gets its configuration from the newrelic.config file, which is generated as part of the install process. By default, only a global newrelic.config file is created, but you can also create app-local newrelic.config files for finer control over a multi-app system. Other ways to set config options include: using environment variables, or setting server-side configuration from the UI. For more on the various config options and what overrides what, see Config settings precedence.
Support for both .NET Framework and .NET Core use the same configuration options and have the same APM features, unless otherwise stated.
If you make changes to the config file and want to validate that it's in the right format, you can check it against the XSD file (for example, at C:\ProgramData\New Relic\.NET Agent\newrelic.xsd for Windows) with any XSD validator.
Importante
For IIS: after you change your newrelic.config or app.config file, perform an IISRESET from an administrative command prompt. Log level adjustments do not require a reset.
Configuration methods and precedence levels
Upon installation, the .NET agent's configuration file (newrelic.config) applies to all monitored applications, but you can configure the agent in other ways. Here's a diagram showing how different configuration options take precedence over one another:
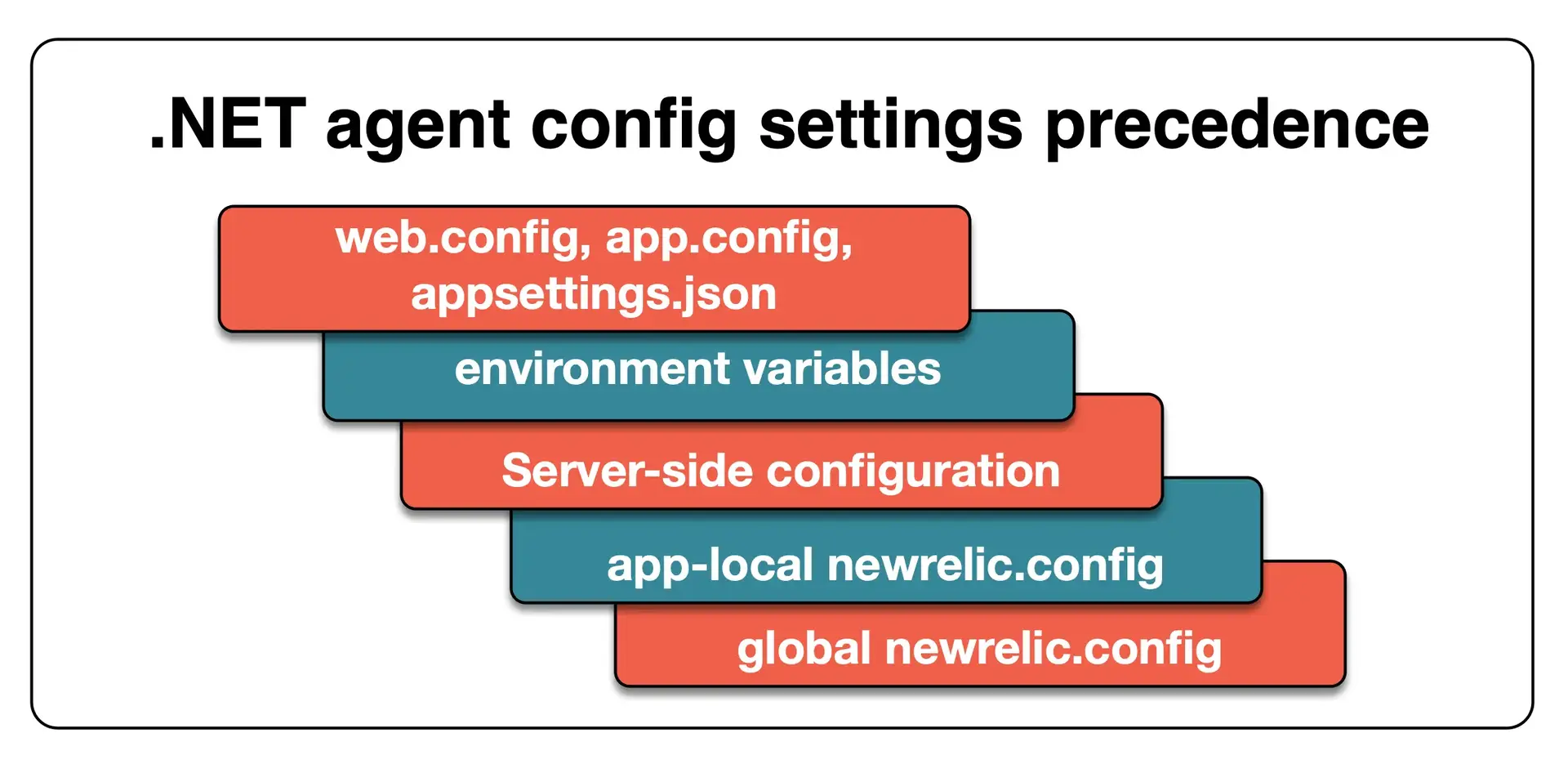
This diagram explains the order of precedence for different ways you might configure the .NET agent.
Here are details about the configuration methods shown in the diagram, and their precedence levels:
.NET configuration | Details and precedence |
|---|---|
| Configuration settings set in these files take highest precedence. If the agent is disabled in the local or global
|
Environment variables | Second-highest precedence. For more about these, see .NET environment variables. |
Server-side configuration | Third-highest precedence. A limited number of server-side configuration settings are available; the other settings will come from other configuration sources. |
App-local | Fourth-highest precedence. You can create app-local The agent looks for app-local config files in the following directories, in this order:
|
Default (global) | Default source and the lowest precedence. Will configure all applications on a host in the absence of other config files. The global config file is located in the New Relic agent home directory: |
Required environment variables
Our .NET agent relies on environment variables to tell the .NET Common Language Runtime (CLR) to attach New Relic to your processes. Some .NET agent install procedures (like the MSI installer) will automatically set these variables for you; some procedures will require you to manually set them.
Cuidado
Security recommendation: You should consider what users can set system environment variables. You should also secure the accounts under which your applications execute to prevent user environment variables overriding system environment variables
If your system has previously used monitoring services (non-New Relic), you may have a "profiler conflict" when trying to install and use the New Relic agent. More details:
For specific install instructions, see the .NET agent install documentation.
Optional environment variables
Some configuration options in New Relic's .NET agent can be set via environment variables as an alternative to setting them in a config file. Below is a list of environment variables recognized by the .NET agent with example values.
NEW_RELIC_LICENSE_KEY=YOUR_LICENSE_KEYNEW_RELIC_APP_NAME=Descriptive NameMAX_TRANSACTION_SAMPLES_STORED=500MAX_EVENT_SAMPLES_STORED=500NEW_RELIC_DISTRIBUTED_TRACING_ENABLED=trueNEW_RELIC_SPAN_EVENTS_ENABLED=falseNEW_RELIC_SPAN_EVENTS_MAX_SAMPLES_STORED=2000NEW_RELIC_INFINITE_TRACING_TRACE_OBSERVER_HOST=myhost.infinitetracing.comNEW_RELIC_LABELS="foo:bar;zip:zap"NEW_RELIC_PROCESS_HOST_DISPLAY_NAME=Custom NameNEW_RELIC_HOST=gov-collector.newrelic.comNEW_RELIC_PROXY_HOST=hostnameNEW_RELIC_PROXY_URI_PATH=path/to/something.aspxNEW_RELIC_PROXY_PORT=5000NEW_RELIC_PROXY_USER=YOUR_USER_NAMENEW_RELIC_PROXY_PASS=YOUR_PROXY_PASSWORDNEW_RELIC_PROXY_DOMAIN=mydomain.comNEW_RELIC_PROXY_PASS_OBFUSCATED=YOUR_OBFUSCATED_PROXY_PASSWORDNEW_RELIC_CONFIG_OBSCURING_KEY=YOUR_OBSCURING_KEYNEW_RELIC_SEND_DATA_ON_EXIT=trueNEW_RELIC_SEND_DATA_ON_EXIT_THRESHOLD_MS=2000NEW_RELIC_HIGH_SECURITY=trueNEW_RELIC_DISABLE_SAMPLERS=trueNEW_RELIC_LOG=MyApp.logNEW_RELIC_LOG_ENABLED=trueNEWRELIC_LOG_LEVEL=infoNEW_RELIC_LOG_CONSOLE=trueNEWRELIC_PROFILER_LOG_DIRECTORY=path\to\a\directory # not configurable via config fileNEWRELIC_LOG_DIRECTORY=path\to\a\directory # Insert a directory where you want to put the agent and profiler logs. You can't set this directory for both agent and profiler logs in the configuration file.NEW_RELIC_LOG_ROLLING_STRATEGY=dayNEW_RELIC_LOG_MAX_FILE_SIZE_MB=100NEW_RELIC_LOG_MAX_FILES=2NEW_RELIC_ERROR_COLLECTOR_IGNORE_ERROR_CODES=401, 403.18NEW_RELIC_ERROR_COLLECTOR_EXPECTED_ERROR_CODES=401, 501-503NEW_RELIC_APPLICATION_LOGGING_ENABLED=trueNEW_RELIC_APPLICATION_LOGGING_METRICS_ENABLED=trueNEW_RELIC_APPLICATION_LOGGING_FORWARDING_ENABLED=trueNEW_RELIC_APPLICATION_LOGGING_FORWARDING_CONTEXT_DATA_ENABLED=trueNEW_RELIC_APPLICATION_LOGGING_FORWARDING_CONTEXT_DATA_INCLUDE="myCustomAttribute1, myOtherCustomAttribute*"NEW_RELIC_APPLICATION_LOGGING_FORWARDING_CONTEXT_DATA_EXCLUDE="myCustomAttribute2, myOtherCustomAttributeMoreSpecificName"NEW_RELIC_APPLICATION_LOGGING_FORWARDING_MAX_SAMPLES_STORED=10000NEW_RELIC_APPLICATION_LOGGING_FORWARDING_LOG_LEVEL_DENYLIST="debug, warn"NEW_RELIC_APPLICATION_LOGGING_LOCAL_DECORATING_ENABLED=trueNEW_RELIC_ALLOW_ALL_HEADERS=trueNEW_RELIC_ATTRIBUTES_ENABLED=trueNEW_RELIC_ATTRIBUTES_INCLUDE=request.headers.*,foo.barNEW_RELIC_ATTRIBUTES_EXCLUDE=request.headers.cookie,request.headers.authorizationNEW_RELIC_UTILIZATION_DETECT_AWS=trueNEW_RELIC_UTILIZATION_DETECT_AZURE=trueNEW_RELIC_UTILIZATION_DETECT_GCP=trueNEW_RELIC_UTILIZATION_DETECT_PCF=trueNEW_RELIC_UTILIZATION_DETECT_DOCKER=trueNEW_RELIC_UTILIZATION_DETECT_KUBERNETES=trueNEW_RELIC_FORCE_NEW_TRANSACTION_ON_NEW_THREAD=trueNEW_RELIC_CODE_LEVEL_METRICS_ENABLED=trueNEW_RELIC_AI_MONITORING_ENABLED=trueNEW_RELIC_AI_MONITORING_RECORD_CONTENT_ENABLED=trueNEW_RELIC_CLOUD_AWS_ACCOUNT_ID=123456789012If you're using New Relic CodeStream to monitor performance from your IDE you may also want to associate repositories with your services and associate build SHAs or release tags with errors.
Errors inbox configuration
Setting one of the following tags will help you identify which versions of your software are producing the errors.
NEW_RELIC_METADATA_SERVICE_VERSIONwill create tags.service.version on event data containing the version of your code that is deployed, in many cases a semantic version such as 1.2.3, but not always.NEW_RELIC_METADATA_RELEASE_TAGwill create tags.releaseTag on event data containing the release tag (such as v0.1.209 or release-209).NEW_RELIC_METADATA_COMMITwill create tags.commit on event data containing the commit sha. The entire sha can be used or just the first seven characters (e.g., 734713b).
An upcoming release of errors inbox will automatically track which versions of your software are producing errors. Any version data will also be displayed in CodeStream.
Setup options, newrelic.config
Use these options to setup and configure your agent via the newrelic.config file. The .NET agent supports the following categories of setup options:
- Configuration element
- Service element
- Obscuring key element
- Proxy element
- Log element
- Application element (configuration)
- Data transmission element
- Host name
Configuration element
The root element of the configuration document is a configuration element.
<configuration xmlns="urn:newrelic-config" agentEnabled="true" maxStackTraceLines="50">The configuration element supports the following attributes:
Service element
The first child of the configuration element is a service element. The service element configures the agent's connection to the New Relic service.
<service licenseKey="YOUR_LICENSE_KEY" sendEnvironmentInfo="true" syncStartup="false" sendDataOnExit="false" sendDataOnExitThreshold="60000" autoStart="true"/>The service element supports the following attributes:
Obscuring key element
The obscuringKey element is an optional child of the service element. The .NET Agent uses this value to deobfuscate supported configuration values. For example, when an obfuscated proxy password is supplied, it will be deobfuscated using this key.
<service licenseKey="YOUR_LICENSE_KEY"> <obscuringKey>OBSCURING_KEY</obscuringKey></service>The obscuring key may also be configured by setting the NEW_RELIC_CONFIG_OBSCURING_KEY environment variable.
Cuidado
Security recommendation: The placement of the obscuring Key in the same configuration file as an obfuscated value may pose a security risk. Consider placing the obscuring key and obfuscated proxy password in environment variables and limiting access to environment variables within your environment.
Proxy element
The proxy element is an optional child of the service element. The proxy element is used when the agent communicates to the New Relic backend service via a proxy.
<service licenseKey="YOUR_LICENSE_KEY"> <proxy host="hostname" port="PROXY_PORT" uriPath="path/to/something.aspx" domain="mydomain.com" user="PROXY_USERNAME" password="PROXY_PASSWORD" passwordObfuscated="OBFUSCATED_PROXY_PASSWORD"/></service>The proxy element supports the following attributes:
Log element
The log element is a child of the configuration element. The log element configures New Relic's logging. The agent generates its own log file to keep its logging information separate from your application's logs.
<log enabled="true" level="info" auditLog="false" console="false" directory="PATH\TO\LOG\DIRECTORY" fileName="FILENAME.log" />The log element supports the following attributes:
Application element (required)
The application element is a child of the configuration element. This required element defines your application name, and disables or enables sampling.
Data transmission element
The dataTransmission element is a child of the configuration element. This element affects how data is sent to New Relic and can be used if you have specific data transmission requirements.
<dataTransmission putForDataSend="false" compressedContentEncoding="deflate"/>The dataTransmission element supports the following attributes:
Host name
If the default host name label in the APM UI is not useful, you can decorate that name in the New Relic UI with a display name. After the application process is restarted and the .NET agent is reporting again, the display name will appear in the Servers drop-down list. This host name setting does not affect the list of hosts on your application's Summary page.
To set a display name, choose one of the following options. The environment variable takes precedence over the config file value. Then restart your application to see your changes in the New Relic UI.
Cloud platform utilization
The utilization configuration element controls how the agent collects utilization information and sends it to the New Relic service to determine pricing. The agent can collect information from Amazon Web Services (AWS) EC2 instances, Docker containers, Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform, Pivotal Cloud Foundry, and Kubernetes.
<configuration . . . > <utilization detectAws="true" detectAzure="true" detectGcp="true" detectPcf="true" detectDocker="true" detectKubernetes="true" /></configuration>The utilization element supports the following attributes:
Instrumentation options
Use these options to configure which elements of your application and environment to instrument. New Relic for .NET supports the following categories of instrumentation options:
Instrumentation element
The instrumentation element is a child of the configuration element. By default, the .NET agent instruments IIS asp worker processes and Microsoft Azure web and worker roles. To instrument other processes, see Instrumenting custom applications.
Rules element (instrumentation)
Importante
This feature is available in .NET Agent 10.21.0 and above.
The rules element is a child of the instrumentation element. The rules element supports any number of ignore child elements, which instructs the Profiler to NOT instrument any methods defined in the specified assembly. Methods defined in other assemblies will still be instrumented.
<instrumentation> <rules> <ignore assemblyName="NameOfAssemblyToIgnore" /> </rules></instrumentation>The ignore rule allows you to optionally define a class name. In the following example, only methods defined in MyNamespace.MyClass in the assembly MyAssembly will be ignored. Other methods in other classes both inside that assembly and within other assemblies will not be ignored by the profiler.
<instrumentation> <rules> <ignore assemblyName="MyAssembly" className="MyNamespace.MyClass" /> </rules></instrumentation>More than one ignore rule can be specified. The following example disables both the Confluent Kafka and StackExchange Redis instrumentations.
<instrumentation> <rules> <ignore assemblyName="Confluent.Kafka" /> <ignore assemblyName="StackExchange.Redis" /> </rules></instrumentation>Please note that custom instrumentation cannot be ignored via the rules element.
Applications element (instrumentation)
The applications element is a child of the instrumentation element. The applications element supports application child elements which specify which non-web apps to instrument. The application element contains a name attribute. Additionally, starting in agent version 10.48.0, there is an optional include attribute with a default value of "true". Set this attribute to "false" to prevent the agent from instrumenting that process.
Importante
This is not the same as the application (configuration) element, which is a child of the configuration element.
<instrumentation> <applications> <application name="MyService1.exe" /> <application name="MyService2.exe" /> <application name="MyService3.exe" include="false" /> </applications></instrumentation>Alternatively, starting in agent version 10.48.0, set the NEW_RELIC_INCLUDED_APPLICATION_NAMES and/or the NEW_RELIC_EXCLUDED_APPLICATION_NAMES environment variable(s) in the application's environment:
NEW_RELIC_INCLUDED_APPLICATION_NAMES="MyService1.exe,MyService2.exe"NEW_RELIC_EXCLUDED_APPLICATION_NAMES="MyService3.exe"Note that exclude takes priority over include.
Attributes element [#agent-attributes]
An attribute is a key/value pair that determines the properties of an event or transaction. Each attribute is sent to APM transaction traces, APM error traces, Transaction events, TransactionError events, Span events, or PageView events. The primary attributes element enables or disables attribute collection for the .NET agent, and defines specific attributes to collect or exclude. You can also configure attribute settings by the specific destination:
In this example, the agent excludes all attributes whose key begins with myApiKey (myApiKey.bar, myApiKey.value) but collects the custom attribute myApiKey.foo.
<attributes enabled="true"><exclude>myApiKey.*</exclude><include>myApiKey.foo</include></attributes>You can view the .NET APM attributes on the .NET agent attributes page. You can also define custom attributes with the agent API call AddCustomAttribute.
Feature options
Use these options to enable, disable, and configure New Relic features. New Relic for .NET allows you to configure the following features:
- App pools
- Error collection
- High-security mode
- Strip exception messages
- Transaction events
- Custom events
- Custom parameters
- Tags/labels
- Browser instrumentation
- Slow Queries
- Transaction traces
- Datastore tracer
- Distributed tracing
- Infinite Tracing
- Cross application traces
- Span events
- Capture HTTP Request Headers
- Application logging
- Code level metrics
- Cloud provider metadata
- AI monitoring
App pools
Importante
This is only applicable to a system's global config file.
Importante
This setting only applies when the IIS hosting model is set to in-process.
The applicationPools element is a child of the configuration element. The applicationPools element specifies for the profiler exactly which application pools to instrument and uses the same name as the IIS application pool name. This configuration element is useful when you may need to instrument only a small subset of your app pools. For example, a given server might have several hundred application pools, but only a few of those pools need to be instrumented by the .NET agent.
Here is an example of disabling instrumentation for specific application pools:
<applicationPools> <applicationPool name="Foo" instrument="false"/> <applicationPool name="Bar" instrument="false"/></applicationPools>Here is an example of disabling instrumentation for all application pools currently executing on the server and enabling instrumentation for specific application pools:
<applicationPools> <defaultBehavior instrument="false"/> <applicationPool name="Foo" instrument="true"/> <applicationPool name="Bar" instrument="true"/></applicationPools>The applicationPools element supports the following elements:
Error collection
The errorCollector element is a child of the configuration element. errorCollector configures error collection, which captures information about uncaught exceptions and sends them to New Relic.
<errorCollector enabled="true" captureEvents="true" maxEventSamplesStored="100"> <ignoreClasses> <errorClass>System.IO.FileNotFoundException</errorClass> <errorClass>System.Threading.ThreadAbortException</errorClass> </ignoreClasses> <ignoreMessages> <errorClass name="System.Exception"> <message>Ignore message</message> <message>Ignore too</message> </errorClass> </ignoreMessages> <ignoreStatusCodes> <code>401</code> <code>404</code> </ignoreStatusCodes> <expectedClasses> <errorClass>System.ArgumentNullException</errorClass> <errorClass>System.ArgumentOutOfRangeException</errorClass> </expectedClasses> <expectedMessages> <errorClass name="System.Exception"> <message>Expected message</message> <message>Expected too</message> </errorClass> </expectedMessages> <expectedStatusCodes>403,500-505</expectedStatusCodes> <attributes enabled="true"> <exclude>myApiKey.*</exclude> <include>myApiKey.foo</include> </attributes></errorCollector>Dica
For an overview of error configuration in APM, see Manage errors in APM.
Importante
expectedClasses, expectedMessages, and expectedStatusCodes configuration settings require .NET agent version 8.31.0.0 or higher.
The errorCollector element supports the following elements and attributes:
High-security mode
The highSecurity element is a child of the configuration element. To enable high-security mode, set this property to true and enable the high security property in the New Relic user interface. Enabling high security turns SSL on; request parameters, custom parameters and HTTP request headers are not collected; strip exception messages is enabled; and queries can't be sent to New Relic in their raw form.
Strip exception messages
The stripExceptionMessages element is a child of the configuration element. To enable strip exception messages, set this property to true. By default, this is set to false, which means that the agent sends messages from all exceptions to the New Relic collector. If you enable high-security mode, this is automatically changed to true, and the agent strips the messages from exceptions.
Transaction events
The transactionEvents element is a child of the configuration element. Use transactionEvents to configure transaction events.
<transactionEvents enabled="true" maximumSamplesStored="10000"> <attributes enabled="true"> <exclude>myApiKey.*</exclude> <include>myApiKey.foo</include> </attributes></transactionEvents>The transactionEvents element supports the following attributes:
Custom events
The customEvents element is a child of the configuration element. Use customEvents to configure custom events.
<customEvents enabled="true" maximumSamplesStored="10000"/>The customEvents element supports the following attributes:
Custom parameters
The customParameters element is a child of the configuration element. Use customParameters to configure custom parameters.
<customParameters enabled="true" />The customParameters element supports the following attributes:
Labels (tags)
The labels element is a child of the configuration element.
This sets tag names and values. The list is a semicolon delimited list of colon-separated name and value pairs. You can also use with the NEW_RELIC_LABELS environment variable. Example:
<labels>foo:bar;zip:zap</labels>NEW_RELIC_LABELS="foo:bar;zip:zap"Browser instrumentation
The browserMonitoring element is a child of the configuration element. browserMonitoring configures in your .NET application. Browser gives you insight your end users' performance experience. This is accomplished by measuring the time it takes for your users' browsers to download and render your webpages by injecting a small amount of JavaScript code into the header and footer of each page.
// If you use both the Exclude and Attribute elements// the Exclude element must be listed first.<browserMonitoring autoInstrument="true"> <requestPathsExcluded> <path regex="url-regex-1"/> <path regex="url-regex-2"/> ... <path regex="url-regex-n"/> </requestPathsExcluded> <attributes enabled="true"> <exclude>myApiKey.*</exclude> <include>myApiKey.foo</include> </attributes></browserMonitoring>The browserMonitoring element supports the following attributes:
Browser instrumentation can also be enabled or disabled via an environment variable:
NEW_RELIC_BROWSER_MONITORING_AUTO_INSTRUMENT= true | 1 | false | 0Slow queries
The slowSql element is a child of the configuration element. slowSql configures capturing information about slow query executions, and captures and obfuscates explain plans for these queries.
<slowSql enabled="true"/>The slowSql element supports the following attribute:
Transaction traces
The transactionTracer element is a child of the configuration element. transactionTracer configures transaction traces. Included in the trace is the exact call sequence of the transactions, including any query statements issued.
<transactionTracer enabled="true" transactionThreshold="apdex_f" recordSql="obfuscated" explainEnabled="true" explainThreshold="500" maxSegments="3000" maxExplainPlans="20"> <attributes enabled="true"> <exclude>myApiKey.*</exclude> <include>myApiKey.foo</include> </attributes> </transactionTracer>The transactionTracer element supports the following attributes:
Datastore tracer
The datastoreTracer element is a child of the configuration element.
<datastoreTracer> <instanceReporting enabled="true" /> <databaseNameReporting enabled="true" /> <queryParameters enabled="false" /></datastoreTracer>The datastoreTracer element supports the following sub-elements:
Distributed tracing
The distributedTracing element is a child of the configuration element.
<distributedTracing enabled="true" excludeNewrelicHeader="false"/>Distributed tracing lets you see the path that a request takes as it travels through a distributed system. It requires .NET agent version 8.6.45.0 or higher and is enabled by default in .NET agents 9.0.0.0 and higher.
Importante
Enabling distributed tracing disables cross application tracing, and has other effects on APM features. Before enabling, read the planning guide.
For more information about setting up distributed tracing, see Enable distributed tracing for your .NET applications.
The distributedTracing element supports the following attributes:
Sampler Configuration
Importante
Sampler configuration is available starting with .NET agent version 10.45.0.
The .NET agent currently supports 4 different sampling algorithms that can be configured for use in distributed tracing:
Sampler Type | Description |
|---|---|
Adaptive Sampler | The original sampling algorithm used by the .NET agent and is enabled by default. Sampling decisions are made at random, with the goal of retaining a configured number of samples per sampling period. |
Trace Id Ratio Based Sampler | An implementation of the Open Telemetry Trace Id Ratio Based Sampler which samples a configured percentage of traces based on the (randomly generated) Trace Id. |
Always On Sampler | As the name implies, this sampler will sample every trace. Note that enabling this sampler can have an impact on application performance and will result in increased data ingest. |
Always Off Sampler | The opposite of Always On; this sampler does not sample any traces. Useful in very specific cases. |
The supported samplers can be configured at multiple levels:
Sampler Level | Description |
|---|---|
Root | This is the sampler that is applied at the beginning of a trace. By default, the Adaptive Sampler is configured as the Root sampler. |
Remote Parent Sampled | This is the sampler that is applied when the trace has a remote parent (i.e., the trace originated in an upstream service) that has been sampled. It can be configured to use, for example, the Always On sampler to ensure that all traces in the current application are sampled. |
Remote Parent Not Sampled | This is the sampler that is applied when a trace has a remote parent (i.e., the trace originated in an upstream service) that was NOT sampled. |
The <sampler> configuration element is a child of the <distributedTracing> element and is structured as follows:
<distributedTracing ... > <sampler> <root> <!-- sampler type --> </root> <remoteParentSampled> <!-- sampler type --> </remoteParentSampled> <remoteParentNotSampled> <!-- sampler type --> </remoteParentNotSampled> </sampler></distributedTracing>For each of the sampler levels, one of the following sampler configurations can be specified:
<default /> <!-- default is a synonym for <adaptive /> --><adaptive /><traceIdRatioBased ratio="0.12" /><alwaysOn /><alwaysOff />The <traceIdRatioBased> element has a required ratio attribute, which is a value between 0.0 and 1.0 specifying the percentage of traces that should be sampled.
Importante
The Adaptive Sampler will be used if there is no configuration specified at a particular sampler level or if the configuration element for that level is not specified at all.
The following environment variables can be used to configure the distributed trace sampler at the various sampler levels, specifying one of the possible values for the sampler type:
NEW_RELIC_DISTRIBUTED_TRACING_SAMPLER_ROOT = default | adaptive | traceIdRatioBased | alwaysOn | alwaysOffNEW_RELIC_DISTRIBUTED_TRACING_SAMPLER_REMOTE_PARENT_SAMPLED = default | adaptive | traceIdRatioBased | alwaysOn | alwaysOffNEW_RELIC_DISTRIBUTED_TRACING_SAMPLER_REMOTE_PARENT_NOT_SAMPLED = default | adaptive | traceIdRatioBased | alwaysOn | alwaysOffIf traceIdRatioBased is specified as the value of one these environment variables, a corresponding environment variable to specify the ratio is also required for the same sampler level:
NEW_RELIC_DISTRIBUTED_TRACING_SAMPLER_ROOT_TRACE_ID_RATIO_BASED_RATIO = 0.12NEW_RELIC_DISTRIBUTED_TRACING_SAMPLER_REMOTE_PARENT_SAMPLED_TRACE_ID_RATIO_BASED_RATIO = 0.12NEW_RELIC_DISTRIBUTED_TRACING_SAMPLER_REMOTE_PARENT_NOT_SAMPLED_TRACE_ID_RATIO_BASED_RATIO = 0.12Span event reporting
Distributed tracing reports span events. Span event reporting is enabled by default, but distributed tracing must be enabled for spans to be reported. To disable span events, choose one of the following options:
Infinite Tracing
Infinite Tracing extends the distributed tracing service by employing a trace observer that is external to the agent. It observes 100% of your application traces across various services and provides actionable data so you can solve issues faster.
To turn on Infinite Tracing, make sure you have .NET agent version 8.30 or higher, and enable distributed tracing. Then add the following additional settings:
<configuration . . . > <distributedTracing enabled="true" /> <infiniteTracing> <trace_observer host="YOUR_TRACE_OBSERVER_HOST" /> </infiniteTracing></configuration>Importante
Infinite Tracing spans can be limited by the transactionTracer.maxSegments setting.
The infiniteTracing element supports the following elements:
Cross application traces
The crossApplicationTracer element is a child of the configuration element. crossApplicationTracer links transaction traces across applications. When linked in a service-oriented architecture, all instrumented applications that communicate with each other via HTTP will now "link" transaction traces with the applications that they call and the applications they are called by. Cross application tracing makes it easier to understand the performance relationship between services and applications.
Importante
Cross application tracing has been deprecated as of v9.0.0 of the agent and disabled by default. It will be removed in a future agent version. To use CAT with v9+ of the agent you must set both crossApplicationTracer.enabled = true and distributedTracing.enabled = false. Enabling distributed tracing will disable cross application tracing.
<crossApplicationTracer enabled="true"/>The crossApplicationTracer element supports the following attribute:
Span events
The spanEvents element is a child of the configuration element. Use spanEvents to configure span events.
<spanEvents enabled="true"> <attributes enabled="true"> <exclude>myApiKey.*</exclude> <include>myApiKey.foo</include> </attributes></spanEvents>The spanEvents element supports the following attributes:
Capture HTTP Request Headers
The allowAllHeaders element is a child of the configuration element. Set this to true to allow the .NET Agent to capture all HTTP request headers and apply them to Span and Transaction events as request.headers.{http-header-name} attributes. Set this to false to only allow the .NET agent to collect the following HTTP request headers:
request.headers.refererrequest.headers.acceptrequest.headers.content-lengthrequest.headers.hostrequest.headers.user-agent
Importante
The allowAllHeaders setting is only available in the .NET Agent version 8.40.0+. When using allowAllHeaders to capture attributes, the captured request header attributes are still being controlled by the root level and destination level attributes settings. Without setting the request.header.* in the include list under the attributes element (see the following), the .NET Agent still filters out all header attributes. The default newrelic.config is set to include the request.header.*.
<allowAllHeaders enabled="true" /><attributes enabled="true"> <include>request.headers.*</include> ...</attributes>The default newrelic.config is also set to explicitly exclude the following HTTP request headers to prevent the .NET Agent collecting unwanted data.
<attributes enabled="true"> <exclude>request.headers.cookie</exclude> <exclude>request.headers.authorization</exclude> <exclude>request.headers.proxy-authorization</exclude> <exclude>request.headers.x-*</exclude></attributes>Application logging
Importante
These configuration options are available only with .NET agent versions 9.7.1 and higher. The options related to context data (custom attributes) are only available in .NET agent versions 10.4.0 and higher.
The applicationLogging element is a child of the configuration element. Use applicationLogging to configure instrumentation of your application's logging activity.
There are three main sub-features:
- Metrics: Collect metrics on the total number of log lines written per harvest cycle (
Logging/lines), as well as the number of log lines written at particular logging levels (for example,Logging/lines/ERROR). - Log forwarding: When enabled, the agent will capture log data and send it to New Relic.
- Context data (via
AddCustomAttribute): When enabled, the agent will capture and forward any custom log attributes. Theincludeandexcludeelements are comma-separated lists of attribute names to include or exclude, following the same rules as other agent attribute configuration. They're both empty by default, which results in all log context data being captured and forwarded. - Log-level filtering: When configured with one or more log levels in a comma-separated list, the agent will prevent messages at those levels from being captured and forwarded.
- Labels: When enabled, the agent adds custom labels to agent-forwarded logs. You can use the
excludeattribute, which is a case-insensitive, comma-separated list of label names. By default, the agent adds custom labels when theexcludeattribute is empty.
- Context data (via
- Local log decoration: When enabled, your existing logs will be decorated with metadata which links logs with other New Relic data, such as errors.
For more details, see our docs on using .NET agent logs in context.
<applicationLogging enabled="true"> <metrics enabled="true" /> <forwarding enabled="true" maxSamplesStored="10000" logLevelDenyList=""> <contextData enabled="false" include="" exclude="" /> <labels enabled="false" exclude="" /> </forwarding> <localDecorating enabled="false" /></applicationLogging>These features can also be configured via environment variables:
NEW_RELIC_APPLICATION_LOGGING_ENABLED=trueNEW_RELIC_APPLICATION_LOGGING_METRICS_ENABLED=trueNEW_RELIC_APPLICATION_LOGGING_FORWARDING_ENABLED=trueNEW_RELIC_APPLICATION_LOGGING_FORWARDING_CONTEXT_DATA_ENABLED=trueNEW_RELIC_APPLICATION_LOGGING_FORWARDING_CONTEXT_DATA_INCLUDE="myCustomAttribute1, myOtherCustomAttribute*"NEW_RELIC_APPLICATION_LOGGING_FORWARDING_CONTEXT_DATA_EXCLUDE="myCustomAttribute2, myOtherCustomAttributeMoreSpecificName"NEW_RELIC_APPLICATION_LOGGING_FORWARDING_MAX_SAMPLES_STORED=10000NEW_RELIC_APPLICATION_LOGGING_FORWARDING_LOG_LEVEL_DENYLIST="debug, warn"NEW_RELIC_APPLICATION_LOGGING_FORWARDING_LABELS_ENABLED=trueNEW_RELIC_APPLICATION_LOGGING_FORWARDING_LABELS_EXCLUDE="label1, label2"NEW_RELIC_APPLICATION_LOGGING_LOCAL_DECORATING_ENABLED=trueThe applicationLogging element supports the following attributes and sub-elements:
Code level metrics
The codeLevelMetrics element is a child of the configuration element. Use codeLevelMetrics to enable code level metrics support in CodeStream via additional instrumented method metadata captured as attributes on span events.
For more details, see our documentation for New Relic CodeStream integration.
<codeLevelMetrics enabled="true" />This can also be configured via environment variable:
NEW_RELIC_CODE_LEVEL_METRICS_ENABLED=trueCloud provider metadata
The cloud element is a child of the configuration element. Use cloud to configure cloud provider metadata for your application.
The cloud element supports the following sub-elements:
AI monitoring
By default, AI monitoring is disabled. To enable AI monitoring, set the enabled attribute to true in the aiMonitoring element. The aiMonitoring element is a child of the configuration element.
Importante
When enabled, AI Monitoring will record a streaming copy of inputs and outputs sent to and from the models you choose to monitor, including any personal information contained therein. When using AI Monitoring, you are responsible for obtaining consent from your model users that their interactions may be recorded by a third party (New Relic) for the purpose of providing the AI Monitoring feature.
<aiMonitoring enabled="true" />This can also be configured via environment variable:
NEW_RELIC_AI_MONITORING_ENABLED=trueThe aiMonitoring element supports the following sub-elements:
Settings in app.config or web.config
For ASP.NET and .NET Framework console apps you can also configure the following settings in your app's app.config or web.config, within the outermost element, <configuration>:
Settings in appsettings.json
For .NET Core apps, you can configure the following settings in appsettings.json if the following is true:
- The
appsettings.jsonfile must be located in the current working directory of the application. - The application must have the following dependencies:
Importante
For ASP.NET Core apps, the .NET Agent will read from appsettings.{environment}.json if you set the ASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENT variable.