With New Relic, you can stay informed about Kubernetes issues by defining the specific data you want to monitor, setting customizable thresholds, and configuring the notifications you want to receive. You can add a set of recommended alert policies that you can tailor to your needs, or you can create completely custom , policies, and workflows to suit your environment.
ヒント
Check out Alerting concepts and terms for more information about how alerts work.
Create a Kubernetes alert condition
Go to one.newrelic.com > All capabilities > Infrastructure and click Alerts on the left navigation pane.
Click + New Alert Condition.
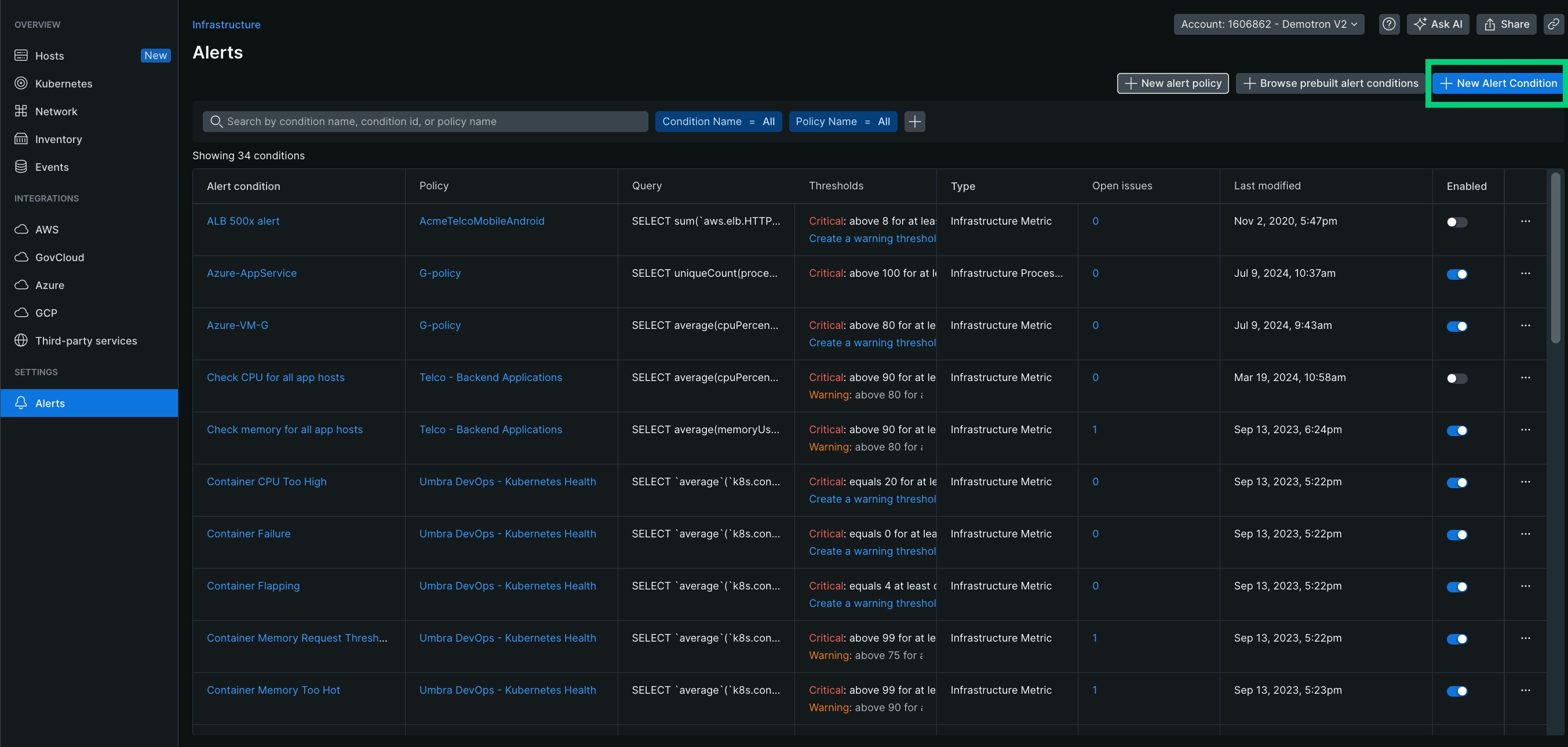
Choose Kubernetes as an alert type and define your thresholds.
Define your thresholds.
Configure your alert policy. You can create a new policy or add this condition to an existing policy.
Set the condition status of the condition.
(Optional) Add a runbook URL.
Click Create.
ヒント
You can also create Kubernetes alerts using a NRQL alert condition.
Create a Kubernetes alert policy
Go to one.newrelic.com > All capabilities > Infrastructure and click Alerts on the left navigation pane.
Click + New alert policy.
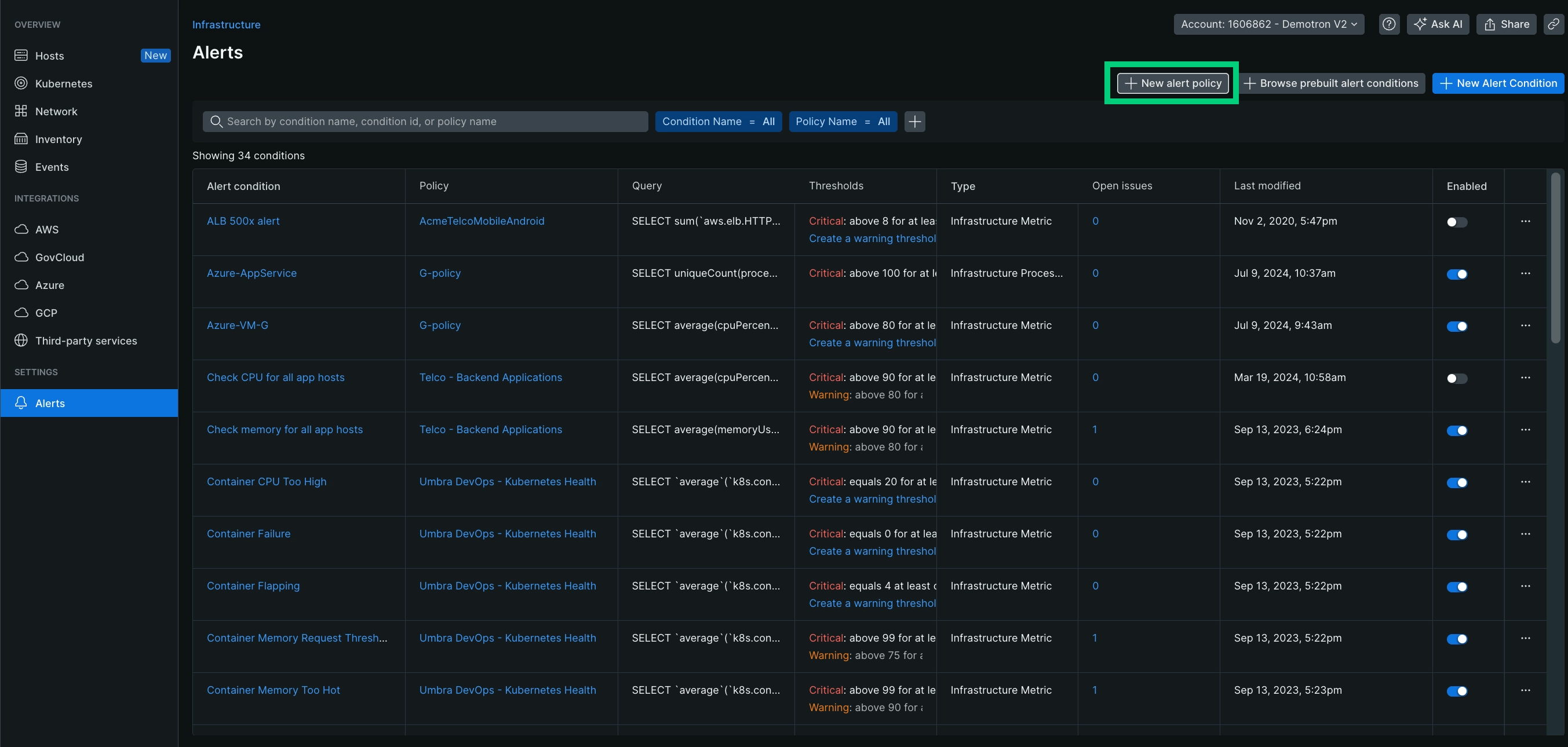
Enter a meaningful name for the policy (maximum 64 characters).
Choose the way you want to group the alert events from this policy.
(Optional) Check the box Suppress noise with machine learning correlation to enable correlation for the alert policy.
Click Set up notifications.
Kubernetes alert notifications
Once you've configured your alert conditions, policies, and workflows, you'll begin to receive notifications when the threshold configured in an alert condition is triggered. You have these options:
Go to a chart of the alert event data by selecting the name of the identifier. The entity identifier that triggered the alert appears near the top of the notification message. The format of the identifier depends on the alert type:
Available pods are less than desired pods alerts:
K8s:CLUSTER_NAME:PARENT_NAMESPACE:replicaset:REPLICASET_NAMECPU or memory usage alerts:
K8s:CLUSTER_NAME:PARENT_NAMESPACE:POD_NAME:container:CONTAINER_NAME
Here are some examples.